Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography
Overview of Data Domain
General Information
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that renders an in vivo cross-sectional view of the retina. OCT utilizes a concept known as interferometry to create a cross-sectional map of the retina that is accurate to within at least 10-15 microns. This technique provides detailed, cross-sectional images of the various layers of the retina with high resolution, enabling clinicians to diagnose and monitor a wide range of retinal diseases and conditions.
How OCT of the retina works and its significance:
-
Imaging Process: OCT of the retina utilizes a low-coherence light source, usually near-infrared light, to capture cross-sectional images of the retina. The light is split into two arms, with one directed towards the retina (sample arm) and the other towards a reference mirror. The reflected light from both arms is then recombined and analyzed to generate an interference pattern.
-
The retina consists of several layers, including: internal limiting membrane, the retinal nerve fiber layer, ganglion cell layer, inner plexiform layer, inner nuclear layer, outer plexiform layer, outer nuclear layer, external limiting membrane, photoreceptor layer (containing rods and cones), retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), and Bruch's membrane. OCT of the retina provides detailed visualization of these layers, allowing clinicians to assess their thickness, integrity, and any abnormalities. Choriocapillaris and choroidal stroma are also visible layers in OCT.
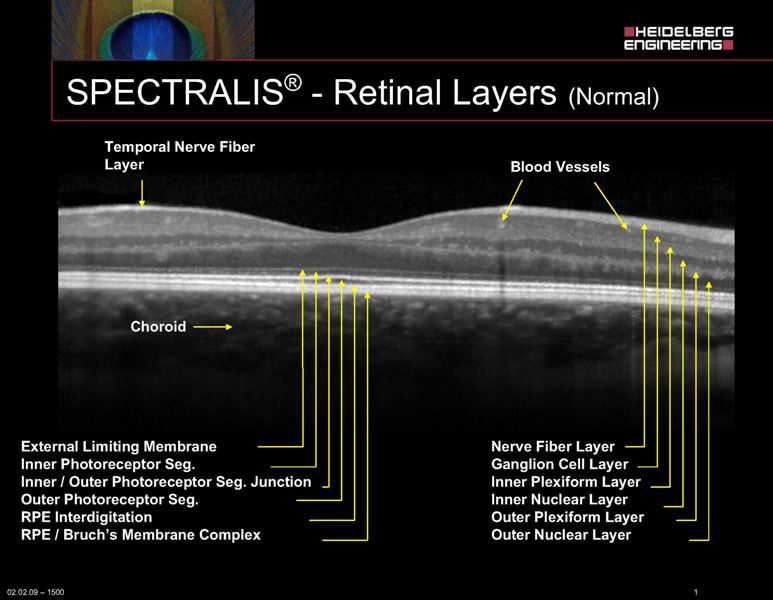
Figure 1. Retinal layers in normal, healthy eye imaged with Hedeilberg Spectralis.
-
Diagnosis and Monitoring: OCT of the retina is widely used in ophthalmology for diagnosing identify structural changes in the retina, such as fluid accumulation, and monitoring various retinal conditions, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy, retinal vein occlusion, macular edema, and glaucoma.
-
Treatment Guidance: OCT of the retina plays a crucial role in guiding treatment decisions for retinal diseases. For example, it helps ophthalmologists determine the need for interventions such as intravitreal injections, laser therapy, or surgical procedures. By monitoring changes in retinal morphology over time, clinicians can assess the efficacy of treatment and adjust management strategies accordingly.
-
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) plays a crucial role in the detection and management of glaucoma, a progressive optic nerve disease characterized by damage to the optic nerve and loss of peripheral vision. OCT provides detailed, quantitative assessments of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) and the optic nerve head (ONH), aiding in the early diagnosis, monitoring, and management of glaucoma.
-
RNFL Thickness Measurement: OCT allows for precise measurement of the thickness of the RNFL, which consists of axons of retinal ganglion cells. Thinning of the RNFL is a hallmark sign of glaucoma and can occur before visual field defects are detectable by conventional perimetry. OCT enables clinicians to quantitatively assess RNFL thickness around the optic nerve head and along the peripapillary region, helping in early detection of glaucoma and monitoring disease progression over time.
-
Optic Nerve Head Assessment: OCT provides detailed imaging of the optic nerve head, including measurements of rim area , cup-to-disc ratio, and neuroretinal rim thickness. Changes in these parameters can indicate structural damage to the optic nerve associated with glaucoma. OCT scans also allow clinicians to visualize and quantify the presence of optic disc hemorrhages, which are often associated with glaucomatous optic nerve damage.
-
Overview of AI-READI Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
| Manufacturer | Manufacturer's Model (device) | Protocol Name | Anatomic Regions* | Width | Height | Number of frames | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heidelberg | Spectralis | Spec-ONH-RC-HR-OCT | Optic Disc | 496 | 768 | 27 | |
| Heidelberg | Spectralis | Spec-MAC-HR-OCT | Macula | 496 | 768 or 1536 | 61 | Two versions of the protocols were used for the pilot but in the future 496, 1536 will be used. |
| Topcon | Maestro2 | Maestro2-3D-Wide | Macula | 885 | 512 | 128 | |
| Topcon | Maestro2 | Maestro2-3D-Macula | Macula | 885 | 512 | 128 | |
| Topcon | Maestro2 | Maestro2-Mac-6x6 | Macula | 885 | 360 | 60 | 6 files have different dimensions (885, 320, 320) |
| Topcon | Triton | Triton-3D(H)+Radial 12x9-OCT | Optic Disc | 992 | 512 | 256 | |
| Topcon | Triton | Triton-Macula 6x6-OCTA | Macula | 992 | 320 | 320 | |
| Topcon | Triton | Triton-Macula 12x12-OCTA | Macula | 992 | 512 | 512 |
*More information on individual files, please refer to manifest.csv within the retinal_oct folder
Example images
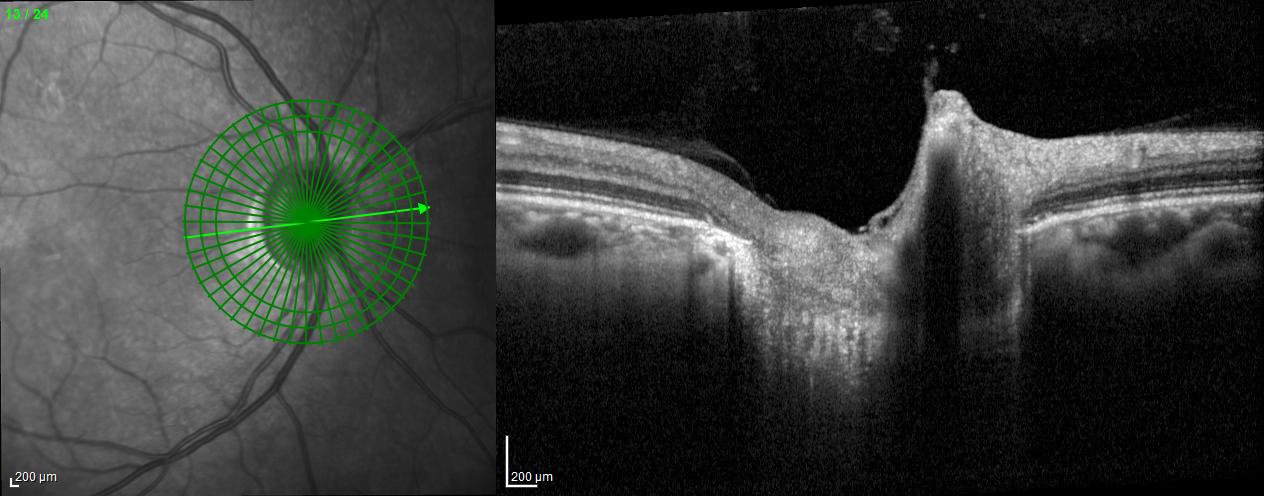
A radial line-scan pattern is part of the ONH-RC scan protocol and allows for assessing the thickness of the neuro-retinal rim based on the detection of the disk margin. From each B-Scan, the shortest distance from Bruch's membrane opening (BMO) to the ILM is determined and indicated by a cyan arrow in the B-Scan. The analysis is therefore called BMO-based minimum rim width (BMO-MRW). It considers the variable geometry of the neural tissue as it exits the eye via the optic nerve head. BMO-MRW data can be classified based on a reference database according to Garway-Heath sectors as well as globally.
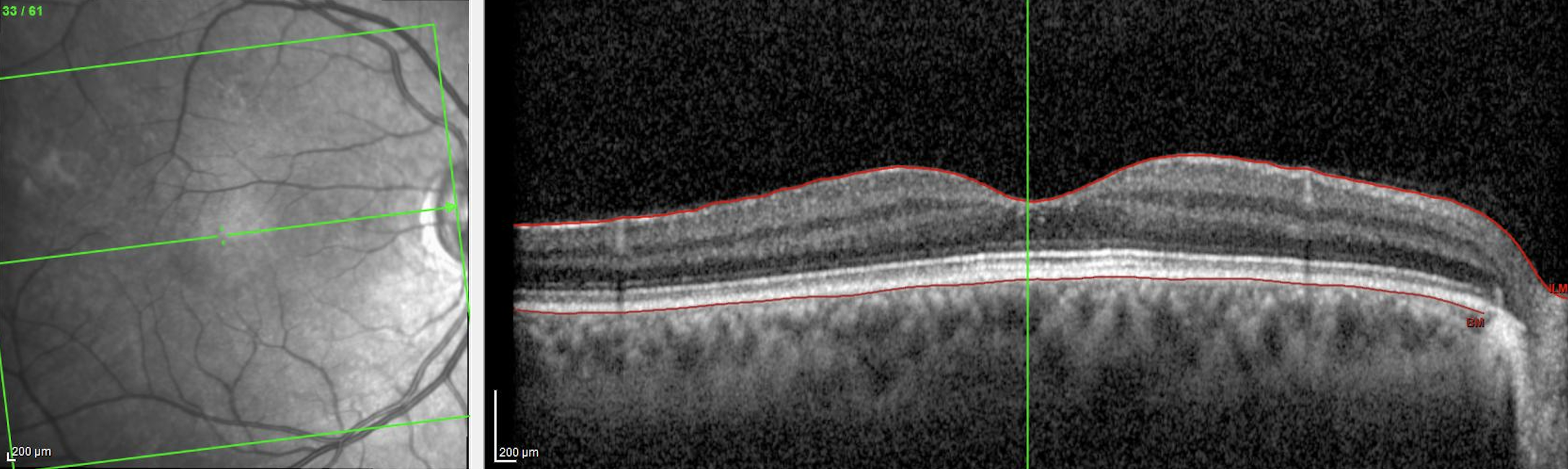
Figure 3. Posterior pole Macula high-resolution OCT (Spec-PPole Mac-HR-61 lines-OCT) Heidelberg Spectralis
The PPoleH scan is a volume scan which is placed on the posterior pole of the eye and which is aligned to the individual Fovea-to-BMO-center axis. Posterior pole horizontal high resolution Macula OCT scan pattern, own source (UCSD)
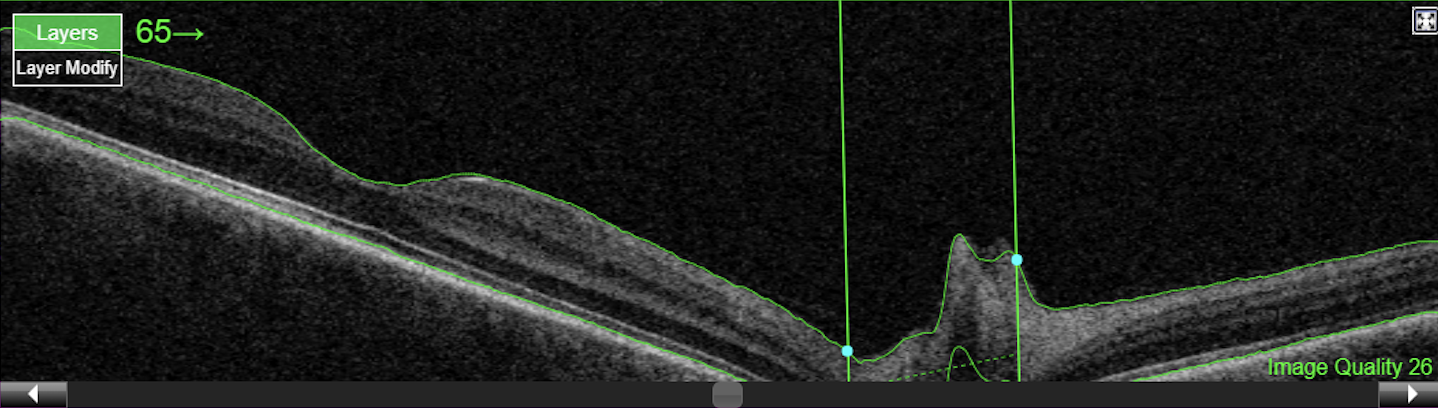
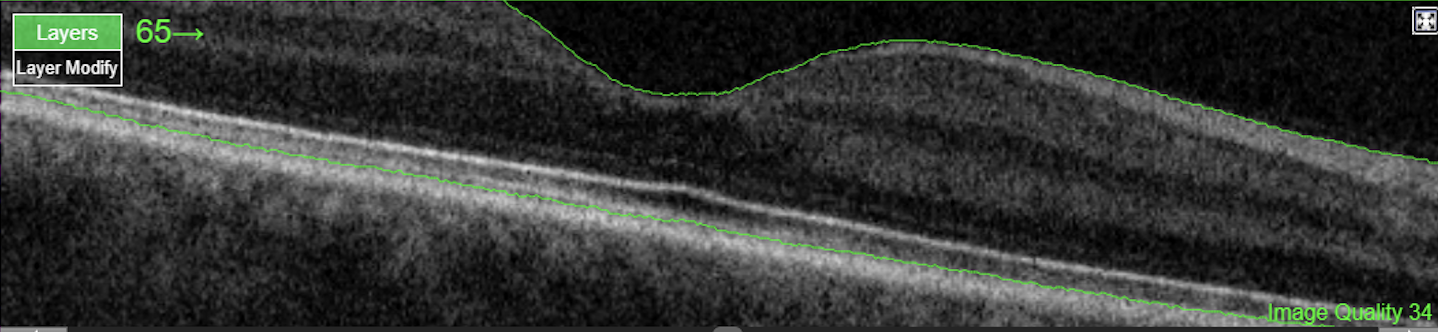
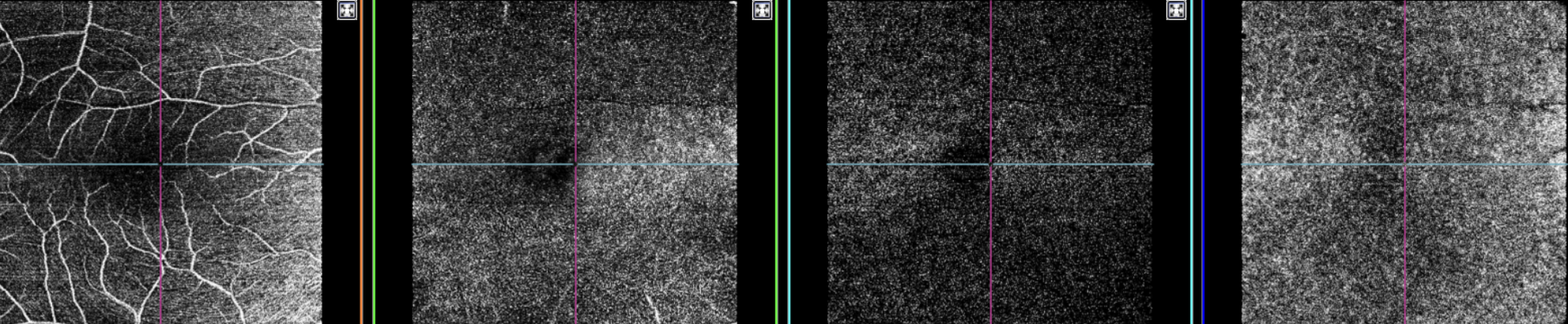
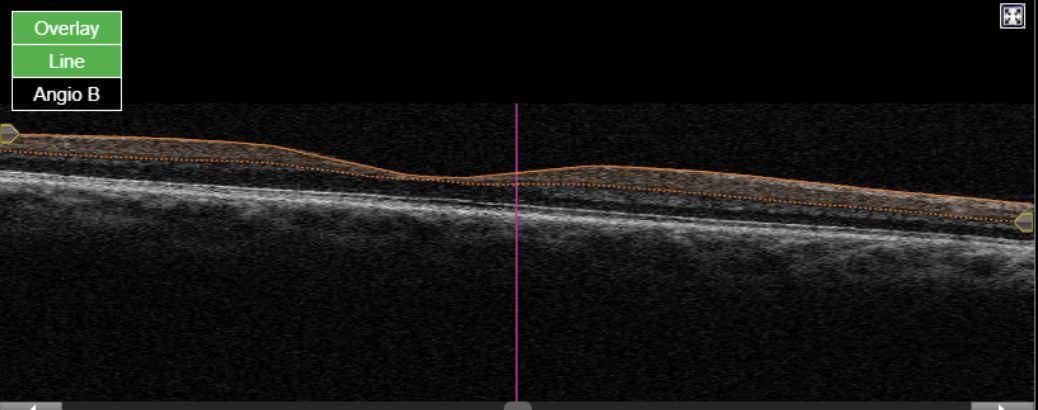
Figure 6. Topcon, Maestro2, Maestro2-Mac 6x6-360x360-(rep3)-OCTA, own source (UCSD), en face (superficial, deep, outer retina and choriocapillaris) and OCT B-scan.
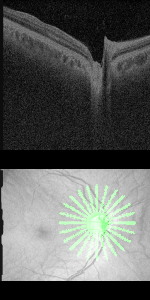
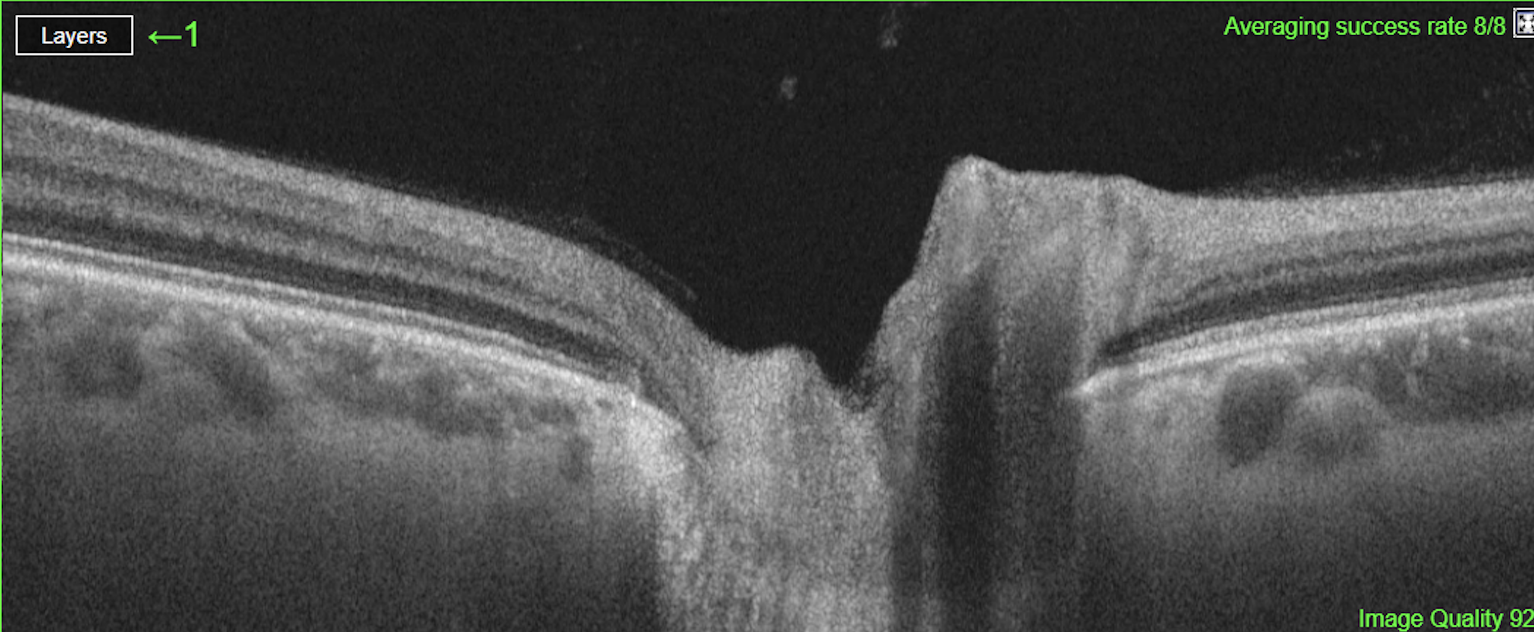

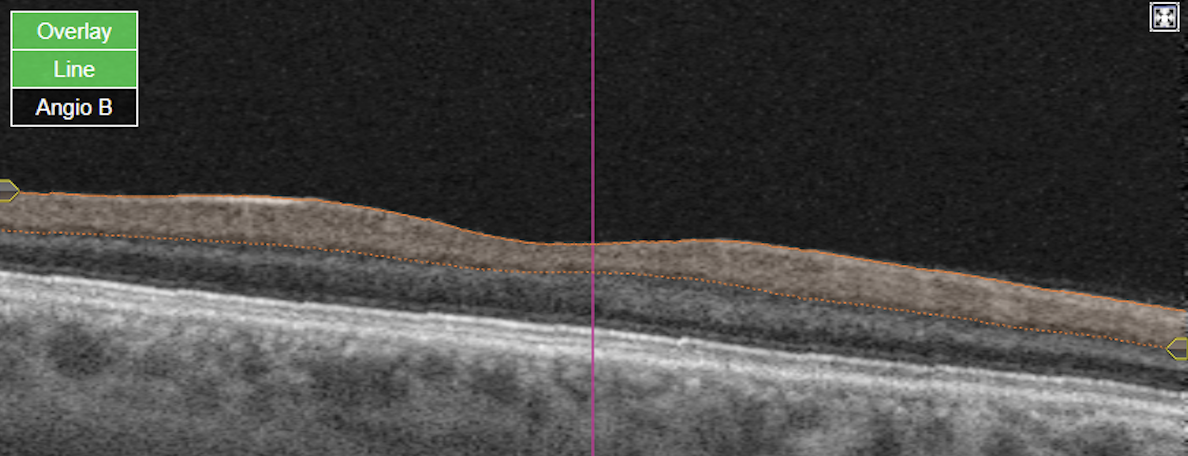
Figure 8. Topcon, Triton, Triton-Macula 6x6-OCTA, own source (UCSD), en face slabs (superficial, deep, outer retina, choriocapillaris) and Angio OCT B-scan
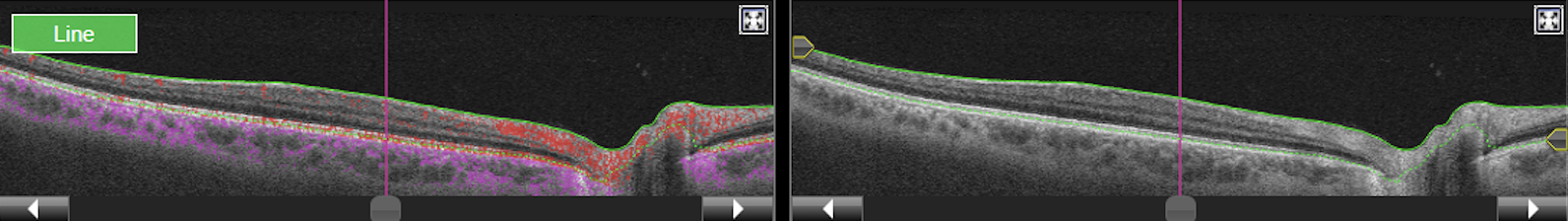
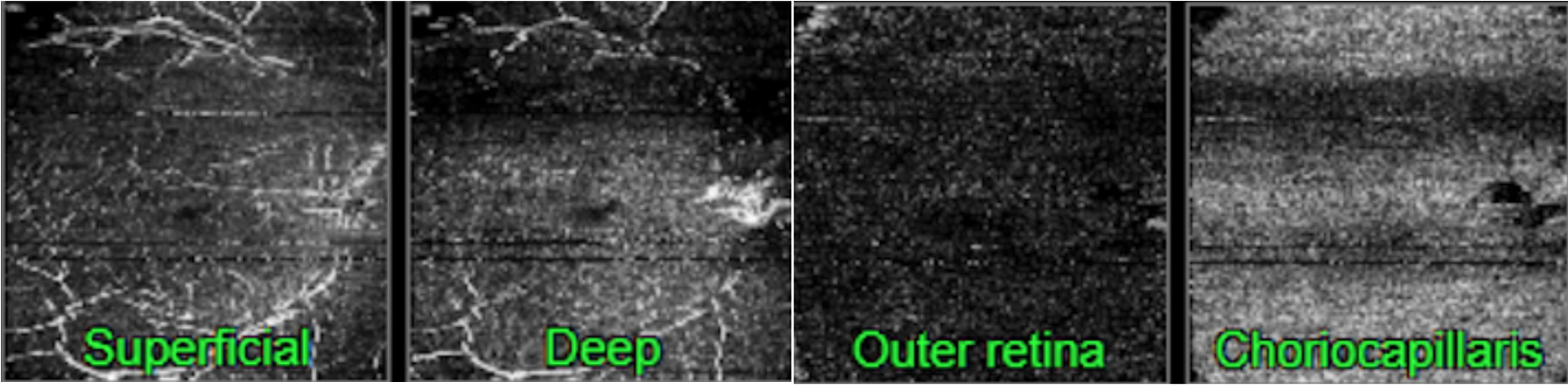
Figure 9. Topcon, Triton, Triton-Macula 12x12-OCTA, own source (UCSD,) structural B-scan and en-face images.
Data Processing
File format
The file format is in DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) which is a technical standard for the digital storage and transmission of medical images and related information.
Data Standard
For all files in retinal_photography, the exported files from the devices were formatted according to the NEMA DICOM standards on Ophthalmic Tomography Image. The detailed information about the tags and values could be found in the hyperlink. All mandatory modules (M) were included, and within the mandatory modules, the tags that are categorized as Type 1 (Tag and value both needed) and Type 2 (tag needed value can be empty) were evaluated and filled in accordingly.
File Processing
Files were processed to comply with the NEMA DICOM standards on Ophthalmic Tomography Image through removing, adding, editing tags and values. Note that tags that are not listed in Ophthalmic Tomography Image and did not provide additional information are removed for consistency and clarity. In addition to ensuring files are NEMA compliant, further processing in the following were done to ensure consistency across the files:
| DICOM Tag Number | DICOM Tag Name | Values | Action, Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0010) | Patient Name | Blank | Removal, Patient information |
| (0010,0030) | Patient Birth Date | Blank | Removal, Patient information |
| (0010,0040) | Patient Sex | A unified value of “M” | Removal, Patient information removed |
| (0008,0090) | Referring Physician Name | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
| (0020, 0010) | Study ID | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
| (0008, 0050) | Accession Number | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
| (0008, 2218) | Anatomic Region Sequence | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
| (0022, 0015) | Anatomic Region Sequence | e.g., 5665001, SCT, Retina | Harmonized, up-to-date information. Based on dicom.nema.org DICOM PS3.16 2024b - Content Mapping Resource B.DCMR Context Groups (Normative) |
| (0022, 0015) | Acquisition Device Type Code Sequence | e.g., 392012008, SCT, Optical Coherence Tomography Scanner | |
| (5200, 9229) | Shared Functional Groups Sequence | Includes these tags within the correct nested structure: - >(0008, 1140) Referenced Image Sequence | Harmonized, Based on this information the nested structures were organized: dicon.nema.org, dicon.innolitics.com |
| >(0008, 9124) | DerivationImageSequence | e.g., empty | Addition,Tag is added for NEMA compliance (Type 2 tag needed value can be empty) |
| >(0008, 0000) | Group Length | e.g., 596 | Removed, Unnecessary information |
| >(5200, 9230) | Group Length | e.g., 596 | Removed, Unnecessary information |
| >(0040, 0000) | Per Frame Functional Groups Sequence | e.g., include these tags within the nested structure >(0020, 9111) Frame Content Sequence | Harmonized, Based on this information the nested structures were organized: diconm.nema.org dicom.innolitics.com |
| >(0020, 0000) | Group Length | e.g., 596 | Removed, Unnecessary information |
| (0020, 9222) | Dimension Index Sequence | e.g., includes tags listed below (0020, 9164), (0020, 9165), (0020,9167) within the nested structure | Harmonized, consistency |
| >(0020, 9164) | Dimension Organization UID | e.g., 2.16.840.1.11 4517.10.5. 3.1.90706312 02401180 9124012 | Harmonized,Consistency and Accurate information Values |
| >(0020, 9165) | Dimension Index Pointer | e.g., 00209056,00209057 | |
| >(0020, 9167) | Functional Group Pointer | e.g., 00209111 | |
| (0022, 000D) | Pupil Dilated | e.g., YES/NO | Addition,Missing value |
| (0022, 0058) | Mydriatic Agent Sequence | e.g., empty | Addition, Missing tag (tag is needed if Pupil Dilated is YES) |
| (0022, 000E) | Degree Of Dilation | e.g., empty | Addition, Missing tag (tag is needed if Pupil Dilated is YES) |
| (0018, 1030) | Protocol Name | e.g., spectralis onh rc hr oct | Addition, Better information delivery |
*Note that tags that are not listed in Ophthalmic Tomography Image IOD Modules and did not provide additional information are removed for consistency and clarity.
> indicates that this is a nested structure within the tag above (e.g., ( 0020, 9164 ) is a within (0020, 9222))
*(0020, 9116) Plane Orientation Sequence, (0028, 9110) Pixel Measures Sequence exists in either Shared Functional Groups Sequence and Per Frame Functional Groups Sequence.
Metadata Example
OCT: spectralis onh rc hr oct
DICOM tags:
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 4 | OPT |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 22 | Heidelberg Engineering |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 10 | Spectralisus |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | spectralis onh rc hr oct |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0028,0008) | Number Of Frames | US | 1 | 2 | 27 |
| (0022,0035) | Depth Spatial Resolution | FL | 1 | 4 | 7 |
| (0028,0010) | Rows | US | 1 | 2 | 496 |
| (0028,0011) | Columns | US | 1 | 2 | 768 |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,0039) | Ophthalmic Image Orientation | CS | 1 | 6 | LINEAR |
OCT: spectralis ppl mc hr oct
DICOM tags:
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 4 | OPT |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 22 | Heidelberg Engineering |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 10 | Spectralisus |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | spectralis onh rc hr oct |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0028,0008) | Number Of Frames | US | 1 | 2 | 60 |
| (0022,0035) | Depth Spatial Resolution | FL | 1 | 4 | 7 |
| (0028,0010) | Rows | US | 1 | 2 | 496 |
| (0028,0011) | Columns | US | 1 | 2 | 768 |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,0039) | Ophthalmic Image Orientation | CS | 1 | 6 | LINEAR |
OCT: maestro2 3d wide oct
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 4 | OPT |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 22 | maestro2 3d wide oct |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0028,0008) | Number Of Frames | US | 1 | 4 | 128 |
| (0022,0035) | Depth Spatial Resolution | FL | 1 | 4 | 6 |
| (0028,0010) | Rows | US | 1 | 2 | 885 |
| (0028,0011) | Columns | US | 1 | 2 | 512 |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,0039) | Ophthalmic Image Orientation | CS | 1 | 6 | LINEAR |
OCT: maestro2 3d macula oct
DICOM tags:
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPT |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 16 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 22 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 2 | maestro2 3d macula oct |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 4 | R/L |
| (0028,0008) | Number Of Frames | US | 1 | 4 | 128 |
| (0022,0035) | Depth Spatial Resolution | FL | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| (0028,0010) | Rows | US | 1 | 2 | 885 |
| (0028,0011) | Columns | US | 1 | 2 | 512 |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| (0022,0039) | Ophthalmic Image Orientation | CS | 1 | 6 | LINEAR |