Retinal OCTA
Overview of Data Domain
Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) is a non-invasive imaging modality that permits visualization of retinal and inner choroidal circulation without the need for the dye injection, based on the principle of mapping red blood cell movement over time by comparing sequential OCT sagittal scans at a given cross-section.
OCT-A technology uses laser light reflectance of the surface of moving red blood cells to accurately depict vessels through different segmented areas of the eye, thus eliminating the need for intravascular dyes. The OCT scan of a patient's retina consists of multiple individual A-scans, which when compiled into a B-scan provides cross-sectional structural information. With OCT-A technology, the same tissue area is repeatedly imaged, and differences are analyzed between scans (over time), thus allowing one to detect zones containing high flow rates (i.e. with marked changes between scans) and zones with slower, or no flow at all, which will be similar among scans. The main advantages are the shorter acquisition time and that it is a non-invasive process. Fluorescein and indocyanine-green angiography require an injectable dye (which takes time to reach retinal vessels, and may be associated with systemic adverse effects and even anaphylactic reactions. One asset of this OCT-based approach is that it provides a quantitative analysis of the retinal vessels (in addition to the qualitative analysis done on standard angiography). Moreover, and contrary to the "2-D" conventional angiograms, OCT-A technology provides "3-D" imaging information of the macula and visualizes peripapillary capillaries that supply the retinal nerve fiber layer.

Images acquired with the SPECTRALIS OCT Angiography Module of the Superficial Vascular Complex, Deep Vascular Complex, and Avascular Complex of the same patient
Clinical applications of OCTA in Retina:
OCT-A has been reported to be useful in the diagnosis and understanding of many retinal conditions, namely:
- Diabetic retinopathy - identifying neovascular complexes, and quantifying foveal avascular zone and nonperfused areas, showing good agreement with fluorescein angiography (FA) findings.
- Dry age-related macular degeneration - a general decrease in choriocapillaris flow has been reported, typically extending beyond the borders of areas of atrophy. Devices using SS-OCT are associated with a better definition of choroidal vasculature changes.
- Wet age-related macular degeneration - qualitative and quantitative analysis of choroidal neovascular membranes (CNVM), being able to classify them, and to follow-up structural changes after intravitreal injections. It has also been raised the potential for detection of these neovascular complexes in non-exudative cases, which would be difficult to detect using SD-OCT or FA, and thus contribute to a more effective and closer follow-up.
- Central serous chorioretinopathy - overlap between findings in FA of a pigmented epithelium detachment (PED) and CNVM may lead to a situation of misdiagnosis. Especially in suspicious cases of flat and irregular PEDs, OCT-A may be helpful in diagnosis and management of CNVM. Although some reports mention a decreased choriocapillaris blood flow, one should pay attention to signal strength in en-face images before interpreting this as hypoperfusion.
- Vascular occlusions - evaluation of nonperfused areas and the integrity of superficial and deep plexus. The preservation of the deep vasculature has been associated with better visual outcomes.
- Macular telangiectasia - identification of the dilated, irregular telangiectatic vessels and, occasionally, the choroidal communication. Since OCT-A does not detect leakage, its combination with the OCT B-scan may help stage and manage MacTel without using FA.
- Choroidal neovascular membranes of miscellaneous causes (e.g. associated with high myopia), with good sensitivity and specificity for detection.
Clinical applications of OCTA in Glaucoma
OCT-A is also gaining increasing importance for optic nerve disorders assessment, such as glaucoma.
It has been reported as a useful tool for evaluating optic disc perfusion in glaucomatous eyes, since attenuated peripapillary and macular vessel density was detectable in pre-perimetric glaucoma patients. Therefore, there is enthusiasm about the role of OCT-A in early detection of glaucomatous damage. Moreover, the quantitative data from these retinal vessels may prove useful in analyzing metabolic activity from the inner layers of the retina and thus provide further advances in monitoring the function and progression of this disease.
It may also prove useful as a tool for ocular blood flow research and thus to help uncover non-IOP-related mechanisms in this disease.
Flow Cube
The acquisition of OCTA volume scans provides a three-dimensional cube of data that includes structural OCT and OCTA images. A series of OCT section images (or B-scans) are acquired in order to create this cube of data.To provide a direct visual correlation of structural and flow information, structural OCT section images and the corresponding blood flow information are combined into a fusion image.This fusion image superimposes the OCTA signal on the structural OCT section image and shows the relation of the respective information.
En Face images
Initial review of the OCTA data is usually based on images that are generated from slabs of the cube. Slabs are sections of 3D volumetric data. In the case of OCTA slabs, the section is delimited by anterior and posterior retinal and choroidal boundaries. The OCTA signal between these boundaries is displayed as a two-dimensional en face image, showing perfused vasculature; It is referred to as “en face image” due to the transversal slab orientation; the resulting image gives the impression of looking onto the retina.
The OCTA and OCT section images offer a detailed and precise correlation between retinal microstructures and perfused vessels. The en face images are optimal for visualization of retinal regions and the associated vascular networks (or plexuses) within specific retinal layers, as defined by slabs. The choice of these delimiting boundaries determines the tissue and associated vasculature that is represented in two-dimensional en face images.
The retinal vascular network can be divided in several vascular plexuses. In order to accurately detect and manage retinal vascular conditions, it is important to precisely discern the different retinal vascular plexuses. It is also important that slabs enable a continuous representation of the retinal and choroidal vasculature so that possible vascular abnormalities are not missed during image review. Currently, the differences in slab definitions often complicate the comparison of en face images between different devices. The en-face slabs are listed for each device and modality in the separate section.They are usually divided into “superficial retina”, “deep retina”, “outer retina”, and “choriocapillaris”.
Segmentation
The segmentation is essential for isolating and analyzing specific vascular plexuses and layers, such as the superficial capillary plexus, deep capillary plexus, and choriocapillaris. Segmentation in OCTA typically relies on automated algorithms that utilize structural OCT images (B-scans) to delineate the boundaries of retinal and choroidal layers. These algorithms identify tissue interfaces, such as the inner limiting membrane, the outer boundary of the outer plexiform layer, or the Bruch's membrane, to define the boundaries of different retinal and choroidal layers accurately. Once the segmentation process is completed, OCTA images can be analyzed and quantified independently for each segmented layer. This allows clinicians and researchers to investigate the microvascular characteristics, perfusion density, and flow dynamics of specific retinal and choroidal regions. Moreover, segmentation facilitates the identification of pathological changes occurring at different depths within the retina and choroid, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various ocular diseases. Considering that slabs are mainly defined by automatically segmented retinal layer boundaries, careful review of the segmentation is critical for correct interpretation of the en face projections. Segmentation failures especially occur in diseases where retinal layers are altered. For instance, intraretinal fluid, large pigment epithelial detachments, choroidal neovascularization, and certain atrophies often cause segmentation errors in most, if not all, state-of-the-art OCTA devices. Higher number of scans within an OCTA volume make the manual correction of such errors for each section image cumbersome. To facilitate the correction of an OCTA volume, i.e. SPECTRALIS OCTA provides a segmentation propagation tool. With this tool, segmentation correction of only a few scans leads to correction of compromised slab boundaries for the entire volume.
Overview of AI-READI Retinal OCTA Data
| Manufacturer | Manufacturer's Model (device) | Protocol Name | Anatomic Regions | Imaging | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topcon | Maestro2 | Maestro2-Mac 6x6-360x360-(rep3)-OCTA | Macula, 6 x 6 | OCTA | Each OCTA scan produces: 1 reference retinal photography file (IR or color photo) 1 OCT (structural scan) file, 2 flow cube files (processed and raw data), 1 heightmap segmentation file, 4 en face images |
| Topcon | Triton | Triton-Macula 6x6-OCTA | Macula, 6 x 6 | OCTA | |
| Topcon | Triton | Triton-Macula 12x12-OCTA | Macula, 12 x 12 | OCTA |
*6 scans of Maestro2 OCTA have different dimensions than the rest. (This includes the associated retinal 6 photography files, 6 structural oct files, 12 flow cube (processed and raw) files, and 6 heightmap segmentation files and 24 en face images)
Flow Cube
| Protocol Name | Height | Width | Number of frames | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maestro2-Mac 6x6-360x360-(rep3)-OCTA | 885 | 360 | 360 | 2 flow cube files (flow cube and flow cube raw data) per OCTA scan |
| Triton-Macula 6x6-OCTA | 992 | 320 | 320 | |
| Triton-Macula 12x12-OCTA | 992 | 512 | 512 |
*Flow cube has two versions (flow cube and flow cube raw data). Flow cube is the processed version of flow cube raw data according to the manufacturer's algorithm. They have the same dimensions.
Segmentation
| Protocol Name | Height | Width | Number of frames | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maestro2-Mac 6x6-360x360-(rep3)-OCTA | 360 | 360 | 9 | 1 segmentation file per OCTA scan |
| Triton-Macula 6x6-OCTA | 320 | 320 | 10 | |
| Triton-Macula 12x12-OCTA | 512 | 512 | 10 |
En Face Images
| Protocol Name | Height | Width | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maestro2-Mac 6x6-360x360-(rep3)-OCTA | 720 | 720 | 4 en face files per OCTA scan |
| Triton-Macula 6x6-OCTA | 640 | 640 | |
| Triton-Macula 12x12-OCTA | 1024 | 1024 |
Example images
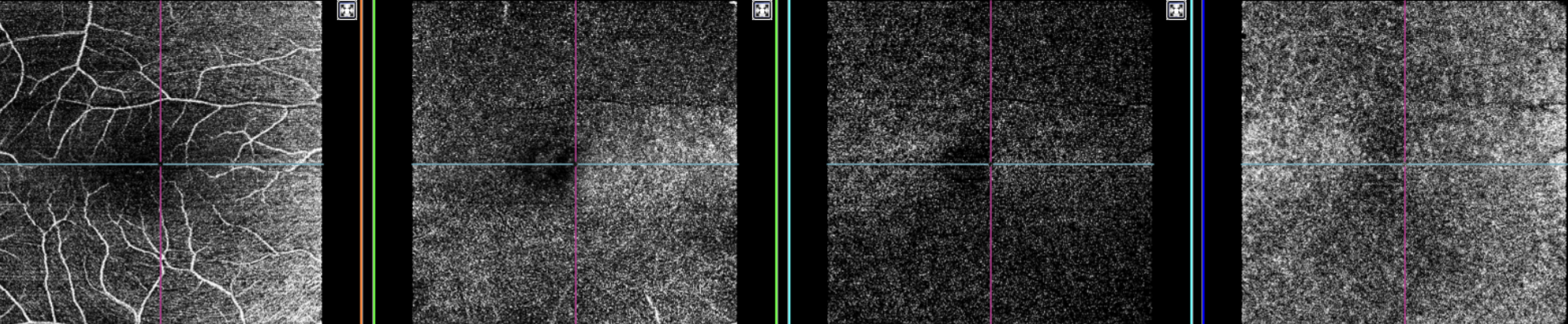
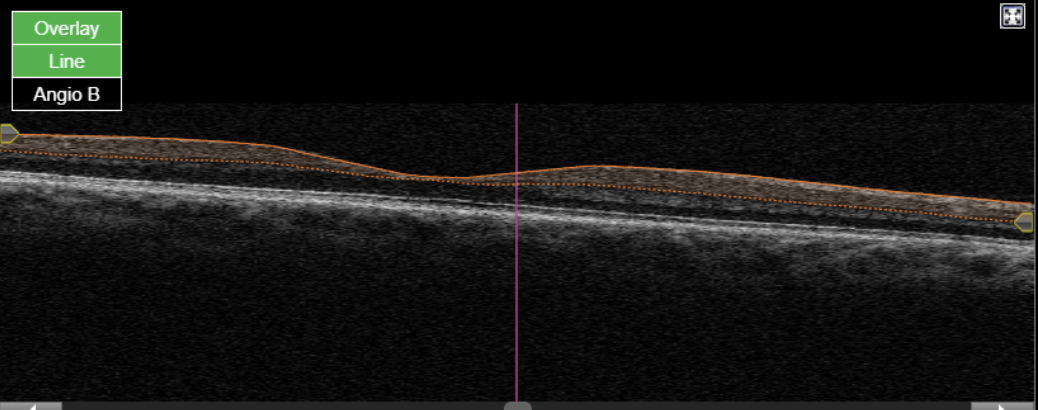
Figure 1. Topcon, Maestro2, Maestro2-Mac 6x6-360x360-(rep3)-OCTA, own source (UCSD), en face (superficial, deep, outer retina and choriocapillaris) and OCT B-scan.

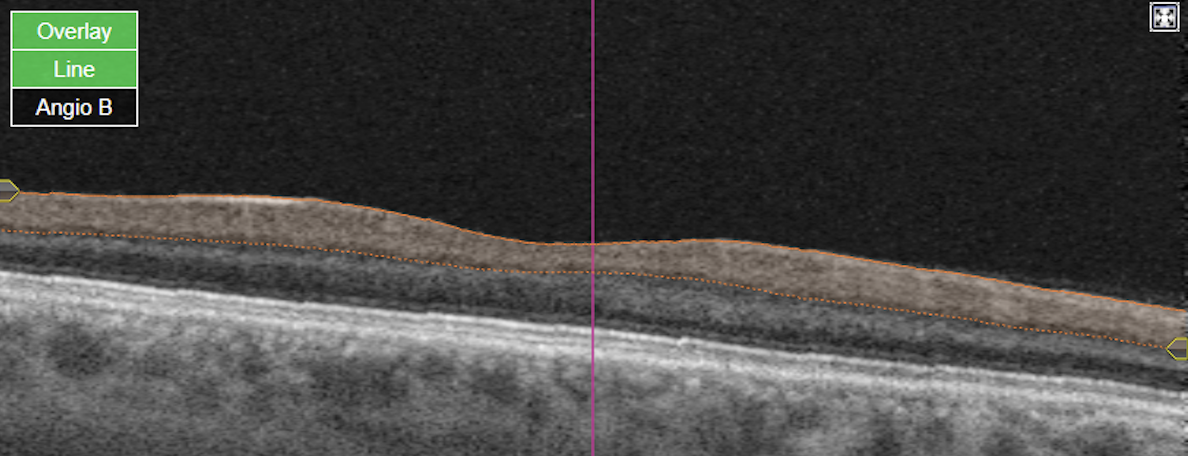
Figure 2. Topcon, Triton, Triton-Macula 6x6-OCTA, own source (UCSD), en face slabs (superficial, deep, outer retina, choriocapillaris) and Angio OCT B-scan.
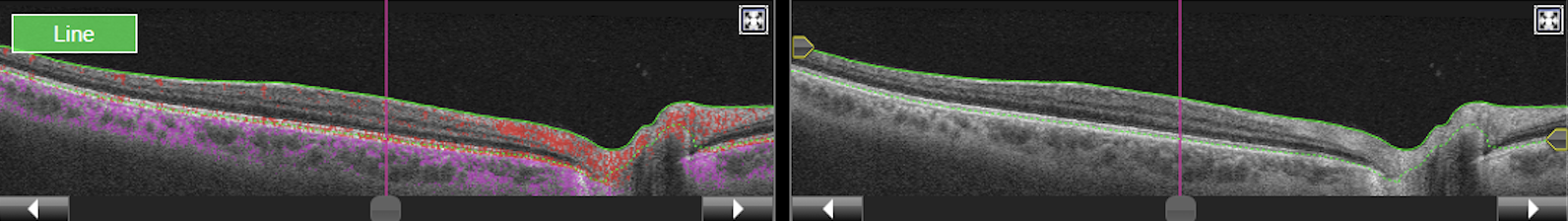
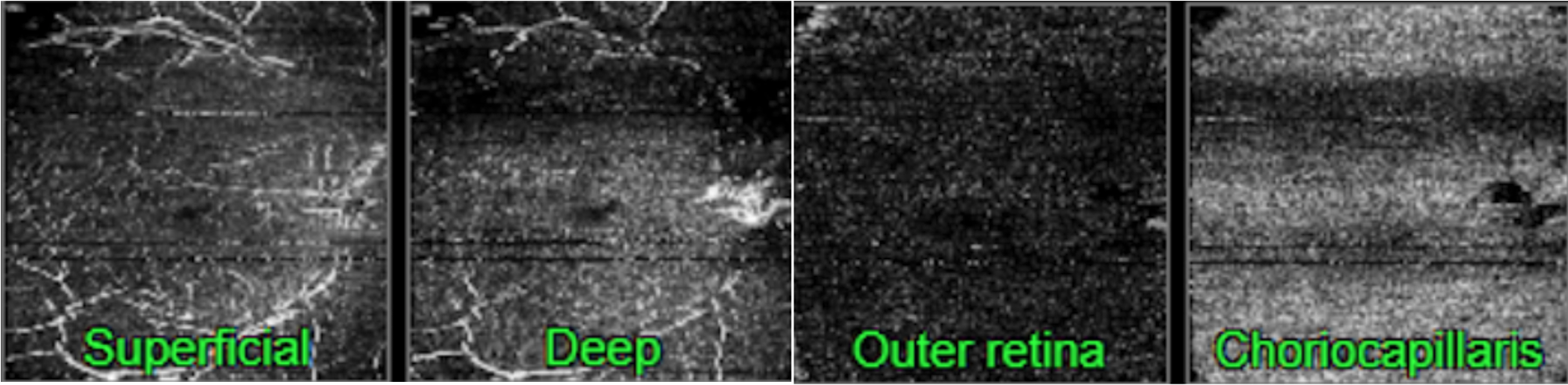
Figure 3. Topcon, Triton, Triton-Macula 12x12-OCTA, own source (UCSD), OCT flow cube and structural B-scan and en-face images.
Data Processing
File format
The file format is in DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) which is a technical standard for the digital storage and transmission of medical images and related information.
Data Standards
Flow Cube
For all files in flow_cube in retinal_octa, the exported files from the devices were formatted according to the NEMA DICOM standards on Ophthalmic Optical Coherence Tomography B-scan Volume Analysis IOD Modules. Initially exported files were fda files. They were first converted to DICOM files using the tool provided by the manufacturer then further formatted to ensure NEMA compliance. The detailed information about the tags and values could be found in the hyperlink. All mandatory modules (M) were included, and within the mandatory modules, the tags that are categorized as Type 1) (Tag and value both needed) and Type 2 (tag needed value can be empty) were evaluated and filled in accordingly.
Segmentation
For all files in segmentation in retinal_octa, the exported files from the devices were formatted according to the NEMA DICOM standards on Supplement 240: Heightmap Segmentation and Revised Ophthalmic OCT En Face Image (Nov 10 2023 version).
Initially exported files were fda files. They were first converted to DICOM files using the tool provided by the manufacturer, which was based on the previous version of segmentation standards. These files were further formatted to ensure NEMA compliance based on Supplement 240: Heightmap Segmentation and Revised Ophthalmic OCT En Face Image (Nov 10 2023 version). The detailed information about the tags and values could be found in the hyperlink. All mandatory modules (M) were included, and within the mandatory modules, the tags that are categorized as Type 1 (Tag and value both needed) and Type 2 (tag needed value can be empty) were evaluated and filled in accordingly.
En Face
For all files in enface in retinal_octa, the exported files from the devices were formatted according to the NEMA DICOM standards on Supplement 240: Heightmap Segmentation and Revised Ophthalmic OCT En Face Image (Nov 10 2023 version).
Initially exported files were fda files. They were first converted to DICOM files using the tool provided by the manufacturer, which was based on the previous version of en face imaging standards. These files were further formatted to ensure NEMA compliance based on Supplement 240: Heightmap Segmentation and Revised Ophthalmic OCT En Face Image (Nov 10 2023 version). The detailed information about the tags and values could be found in the hyperlink. All mandatory modules (M) were included, and within the mandatory modules, the tags that are categorized as Type 1 (Tag and value both needed) and Type 2 (tag needed value can be empty) were evaluated and filled in accordingly.
File Processing
Files were processed to comply with the NEMA DICOM standards listed above through removing, adding, editing tags and values.
Note that tags that are not listed in NEMA DICOM standards listed above and did not provide additional information are removed for consistency and clarity.
In addition to ensuring files are NEMA compliant, further processing in the following were done to ensure consistency across the files:
Flow Cube
| DICOM Tag Number | DICOM Tag Name | Values | Action, Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0010) | Patient Name | Blank | Removal, Patient information |
| (0010,0030) | Patient Birth Date | Blank | Removal, Patient information |
| (0010,004) | Patient Sex | A unified value of “M” | Removal, Patient information removed |
| (0008,0090) | Referring Physician Name | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
| (0020, 0010) | Study ID | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
| (0008, 0050) | Accession Number | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
Segmentation
| DICOM Tag Number | DICOM Tag Name | Values | Action, Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0010) | Patient Name | Blank | Removal, Patient information |
| (0010,0030) | Patient Birth Date | Blank | Removal, Patient information |
| (0010,0040) | Patient Sex | A unified value of “M” | Removal, Patient information removed |
| (0008,0090) | Referring Physician Name | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
| (0020, 0010) | Study ID | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
| (0008, 0050) | Accession Number | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
| (5200, 9229) | Shared Functional Groups Sequence | Includes these tags within the correct nested structure: > (0008, 1140) Referenced Image Sequence | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| (5200, 9230) | Per Frame Functional Groups Sequence | e.g., include these tags within the nested structure
> (0020, 9111) Frame Content Sequence | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| (0028, 0002) | Samples Per Pixel | e.g., 1 | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| (0028, 0004) | Photometric Interpretation | e.g., MONOCHROME | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| (0028, 0010) | Rows | e.g., 360 | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| (0028, 0011) | Columns | e.g., 360 | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| (0028, 0100) | Bits Allocated | e.g., 32 | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| (0028, 0008) | Number Of Frames | e.g., 9 | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| (0062, 0001) | Segmentation Type | e.g., HEIGHTMAP | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| (0008, 0008) | Image Type | e.g., DERIVED, PRIMARY | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| (0020, 9222) | Dimension Index Sequence | e.g., includes tags listed below (0020, 9164), (0020, 9165), (0020,9167) within the nested structure | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| >(0020, 9164) | Dimension Organization UID | e.g., 2.16.840.1.114517.10.5.3.1. 90706312024011809124012 | Values '00209056', '00209057', '00209111' these are pointing to the values of tags within the same file |
| >(0020, 9165) | Dimension Index Pointer | e.g., 00209056,00209057 | |
| >(0020, 9167) | Functional Group Pointer | e.g., 00209111 | |
| (7FE0, 0008) | Float Pixel Data | Initially segmentation standards was based on surface mesh module. Based on the relevant information from these tags (e.g., (0006, 0002) Surface Sequence had information on (0066, 0011) Surface Points Sequence, (0066, 0015) Number of surface points, and (0066, 90016) Point Coordinates Data), the heightmap based segmentation pixel array was made available, formatted, and added to Float Pixel Data. | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| (0018, 1030) | Protocol Name | e.g., maestro2 macula 6x6 octa | Addition, Better information delivery |
En Face
| DICOM Tag Number | DICOM Tag Name | Values | Action, Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0010) | Patient Name | Blank | Removal, Patient information |
| (0010,0030) | Patient Birth Date | Blank | Removal, Patient information |
| (0010,0040) | Patient Sex | A unified value of “M” | Removal, Patient information removed |
| (0008,0090) | Referring Physician Name | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
| (0020, 0010) | Study ID | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
| (0008, 0050) | Accession Number | Blank | Removal, Unnecessary information and inconsistent across devices |
| (0022, 1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | e.g., 128273 DCM Choriocapillaris vasculature flow | Harmonized, up-to-date information Based on https://dicom.nema.org /medical/dicom/ current/output/chtml /part16/PS3.16.html DICOM PS3.16 2024b - Content Mapping Resource B.DCMR Context Groups (Normative) |
| (0022, EEE0) | En Face Volume Descriptor Sequence | e.g., Includes these tags within the correct nested structure: >(0022EEE1) En Face Volume Descriptor Scope>(0022EEE2)Referenced Segmentation Sequence | Added, up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA. |
| (0008, 1115) | Referenced Series Sequence | e.g., Includes these tags within the correct nested structure: >(0008114A)Referenced Instance Sequence >(0020000D)StudyInstanceUID>>(0020000E)SeriesInstanceUID | Added,up-to-date standards listed in Supplement 240 provided by NEMA |
| (0020, 0020) | Patient Orientation | e.g., L, F | Added, Consistency and bettery information delivery |
| (0018, 1030) | Protocol Name | e.g., maestro2 macula 6x6 octa | Addition, Better information delivery |
Metadata Example
OCT: maestro2 macula 6x6 octa
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 4 | OPT |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | maestro2 macula 6x6 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0028,0008) | Number Of Frames | US | 1 | 4 | 360 |
| (0022,0035) | Depth Spatial Resolution | FL | 1 | 4 | 6 |
| (0028,0010) | Rows | US | 1 | 2 | 885 |
| (0028,0011) | Columns | US | 1 | 2 | 360 |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,0039) | Ophthalmic Image Orientation | CS | 1 | 6 | LINEAR |
EN-FACE: maestro2 macula 6x6 octa Superficial Retina Vasculature Flow
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTENF |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | maestro2 macula 6x6 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0022,1624) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point X Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 349 |
| (0022,1626) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point Y Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 386 |
| (0020,4000) | Image Comments | LT | 1 | 28 | Superficial, TOP+0, GCL+15.6 |
| (0022,1616) | Ophthalmic Image Type Description | LO | 1 | 50 | Superficial - Superficial Retina Vasculature Flow |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | SQ | 1 | 78 |
EN-FACE: maestro2 macula 6x6 octa Deep retina vasculature flow
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTENF |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | maestro2 macula 6x6 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0022,1624) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point X Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 349 |
| (0022,1626) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point Y Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 386 |
| (0020,4000) | Image Comments | LT | 1 | 24 | Deep, GCL+15.6, GCL+70.2 |
| (0022,1616) | Ophthalmic Image Type Description | LO | 1 | 36 | Deep - Deep retina vasculature flow |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | SQ | 1 | 70 |
EN-FACE: maestro2 macula 6x6 octa Deep retina vasculature flow
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTENF |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | maestro2 macula 6x6 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0022,1624) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point X Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 349 |
| (0022,1626) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point Y Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 386 |
| (0020,4000) | Image Comments | LT | 1 | 40 | Choriocapillaris, OS/RPE+0, OS/RPE+20.8 |
| (0022,1616) | Ophthalmic Image Type Description | LO | 1 | 52 | Choriocapillaris -Choriocapillaris vasculature flow |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | SQ | 1 | 76 |
EN-FACE: maestro2 macula 6x6 octa Outer retina vasculature flow
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTENF |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | maestro2 macula 6x6 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0022,1624) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point X Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 349 |
| (0022,1626) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point Y Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 386 |
| (0020,4000) | Image Comments | LT | 1 | 38 | Outer Retina (PAR), GCL+70.2, OS/RPE+0 |
| (0022,1616) | Ophthalmic Image Type Description | LO | 1 | 44 | OuterRetina - Outer retina vasculature flow |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | SQ | 1 | 72 |
FLOW CUBE: maestro2 macula 6x6 octa
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTBSV |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | maestro2 macula 6x6 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0028,0008) | Number Of Frames | US | 1 | 4 | 360 |
| (0022,1642) | Number Of Bscans Per Frame | UL | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| (0028,0010) | Rows | US | 1 | 2 | 885 |
| (0028,0011) | Columns | US | 1 | 2 | 360 |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
Link to the imaging protocol: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1gwpoJlYLH6jaoxQ1WDhERHRTLiJnrgk7/edit
OCT: triton 3d radial oct
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 2 | OPT |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 12 | Triton plus |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 20 | triton 3d radial oct |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0028,0008) | Number Of Frames | US | 1 | 2 | 256 |
| (0022,0035) | Depth Spatial Resolution | FL | 1 | 4 | 8 |
| (0028,0010) | Rows | US | 1 | 2 | 992 |
| (0028,0011) | Columns | US | 1 | 2 | 512 |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,0039) | Ophthalmic Image Orientation | CS | 1 | 6 | LINEAR |
OCT: triton macula 6x6 octa
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 4 | OPT |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 12 | Triton plus |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 22 | triton macula 6x6 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0028,0008) | Number Of Frames | US | 1 | 4 | 320 |
| (0022,0035) | Depth Spatial Resolution | FL | 1 | 4 | 8 |
| (0028,0010) | Rows | US | 1 | 2 | 992 |
| (0028,0011) | Columns | US | 1 | 2 | 320 |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,0039) | Ophthalmic Image Orientation | CS | 1 | 6 | LINEAR |
EN-FACE triton macula 6x6 octa Superficial Retina Vasculature Flow
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTENF |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 22 | triton macula 6x6 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0022,1624) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Refe1r1ence Point X Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 309 |
| (0022,1626) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point Y Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 313 |
| (0020,4000) | Image Comments | LT | 1 | 28 | Superficial, TOP+0, GCL+15.6 |
| (0022,1616) | Ophthalmic Image Type 1Description | LO | 1 | 50 | Superficial - Superficial Retina Vasculature Flow |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | SQ | 1 | 72 |
EN-FACE triton macula 6x6 octa Deep retina vasculature flow
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTENF |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 22 | triton macula 6x6 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0022,1624) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point X Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 309 |
| (0022,1626) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point Y Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 313 |
| (0020,4000) | Image Comments | LT | 1 | 24 | Deep, GCL+15.6, GCL+70.2 |
| (0022,1616) | Ophthalmic Image Type Description | LO | 1 | 36 | Deep - Deep retina vasculature flow Vasculature Flow |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | SQ | 1 | 70 |
EN-FACE triton macula 6x6 octa Choriocapillaris vasculature flow
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTENF |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 22 | triton macula 6x6 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0022,1624) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point X Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 309 |
| (0022,1626) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point Y Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 313 |
| (0020,4000) | Image Comments | LT | 1 | 40 | Choriocapillaris, OS/RPE+0, OS/RPE+20.8 |
| (0022,1616) | Ophthalmic Image Type Description | LO | 1 | 52 | Choriocapillaris - Choriocapillaris vasculature flow |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | SQ | 1 | 76 |
EN-FACE triton macula 6x6 octa Outer retina vasculature flow
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTENF |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 22 | triton macula 6x6 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0022,1624) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point X Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 309 |
| (0022,1626) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point Y Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 313 |
| (0020,4000) | Image Comments | LT | 1 | 38 | Choriocapillaris, OS/RPE+0, OS/RPE+20.8 |
| (0022,1616) | Ophthalmic Image Type Description | LO | 1 | 44 | Choriocapillaris - Choriocapillaris vasculature flow |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| (0022,1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | SQ | 1 | 72 |
FLOW CUBE: triton macula 6x6 octa
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTBSV |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 12 | Triton plus |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 22 | triton macula 6x6 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0028,0011) | Columns | US | 1 | 2 | 320 |
| (0028,0010) | Rows | US | 1 | 2 | 992 |
OCT: triton macula 12x12 octa
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 4 | OPT |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 12 | Triton plus |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | triton macula 12x12 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0028,0008) | Number Of Frames | US | 1 | 4 | 512 |
| (0022,0035) | Depth Spatial Resolution | FL | 1 | 4 | 8 |
| (0028,0010) | Rows | US | 1 | 2 | 992 |
| (0028,0011) | Columns | US | 1 | 2 | 512 |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,0039) | Ophthalmic Image Orientation | CS | 1 | 6 | LINEAR |
EN-FACE triton macula 12x12 octa Superficial Retina Vasculature Flow
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTENF |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 22 | triton macula 12x12 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0022,1624) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point X Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 513 |
| (0022,1626) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point Y Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 469 |
| (0020,4000) | Image Comments | LT | 1 | 28 | Superficial, TOP+0, GCL+15.6 |
| (0022,1616) | Ophthalmic Image Type Description | LO | 1 | 50 | Superficial - Superficial Retina Vasculature Flow |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | SQ | 1 | 78 |
EN-FACE triton macula 12x12 octa Deep retina vasculature flow
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTENF |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | triton macula 12x12 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0022,1624) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point X Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 513 |
| (0022,1626) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point Y Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 469 |
| (0020,4000) | Image Comments | LT | 1 | 24 | Deep, GCL+15.6, GCL+70.2 |
| (0022,1616) | Ophthalmic Image Type Description | LO | 1 | 36 | Deep - Deep retina vasculature flow |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | SQ | 1 | 70 |
EN-FACE triton macula 12x12 octa Choriocapillaris vasculature flow
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTENF |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | triton macula 12x12 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0022,1624) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point X Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 513 |
| (0022,1626) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point Y Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 469 |
| (0020,4000) | Image Comments | LT | 1 | 40 | Choriocapillaris, OS/RPE+0, OS/RPE+20.8 |
| (0022,1616) | Ophthalmic Image Type Description | LO | 1 | 52 | Choriocapillaris - Choriocapillaris vasculature flow |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| (0022,1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | SQ | 1 | 76 |
EN-FACE triton macula 12x12 octa Outer retina vasculature flow
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTENF |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 16 | 3DOCT-1Maestro2 |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | triton macula 12x12 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 1 | 2 | R/L |
| (0022,1624) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point X Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 513 |
| (0022,1626) | Ophthalmic Anatomic Reference Point Y Coordinate | FL | 1 | 4 | 469 |
| (0020,4000) | Image Comments | LT | 1 | 38 | Outer Retina (PAR), GCL+70.2, OS/RPE+0 |
| (0022,1616) | Ophthalmic Image Type Description | LO | 1 | 44 | OuterRetina - Outer retina vasculature flow |
| (0028,0100) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,1615) | Ophthalmic Image Type Code Sequence | SQ | 1 | 72 |
FLOW CUBE: triton macula 12x12 octa
| Group/Element | TAG Description | VR | VM | Length | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0010,0020) | Patient ID | LO | 1 | 4 | eg. 1001 (value will differ) |
| (0008,0060) | Modality | CS | 1 | 6 | OPTBSV |
| (0008,0070) | Manufacturer | LO | 1 | 6 | Topcon |
| (0008,1090) | Manufacturer Model Name | LO | 1 | 12 | Triton plus |
| (0018,1030) | Protocol Name | LO | 1 | 24 | triton macula 12x12 octa |
| (0020,0062) | Image Laterality | CS | 2 | 2 | R/L |
| (0028,0008) | Bits Allocated | US | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| (0022,0035) | Columns | US | 1 | 2 | 512 |
| (0028,0010) | Rows | US | 1 | 2 | 992 |
Additional resources
Consider starting with our example Jupyter notebooks to explore the dataset further.